
- #ALKENE HYDROCARBON WITH 6 CARBONS AND DOOBLE BONDS HOW TO#
- #ALKENE HYDROCARBON WITH 6 CARBONS AND DOOBLE BONDS SERIES#
In simpler compounds, you can also add the number before the root for the carbon chain length, so but-1-ene could be 1-butene. Identify which carbon in the chain the alkene begins at, and use this number with '–ene' as the suffix.Count the carbon chain length to find the base of the compound's name.Alkene double bonds are named similarly to branches in an alkane:.See the table below for the first five alkenes. Using the nomenclature in Organic chemistry introduction, we can name simple alkenes.This is an important test for a double bond because alkanes do not have a double bond so bromine does not react with it.With ethene, this reaction has the equation: A colorless dibromoalkane product forms in their place. The double bond in the alkene molecule reacts with a bromine molecule and opens up in an addition reaction, using both reactant molecules up. The brown color caused by bromine water disappears because bromine (Br2) is being reacted away.

We say that alkenes decolorize bromine water.
#ALKENE HYDROCARBON WITH 6 CARBONS AND DOOBLE BONDS SERIES#
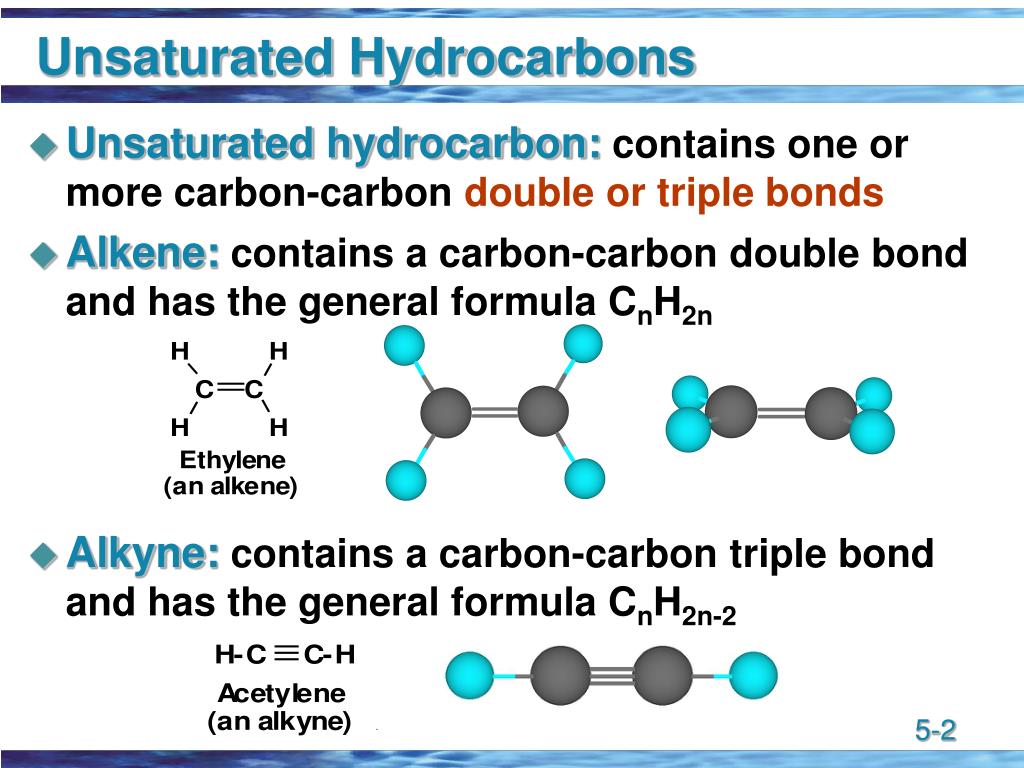
Like alkanes, alkenes are another homologous series of hydrocarbons. This means that not all the bonds made by carbon are single bonds, they also contain double or triple bonds, to either carbon or another atom. However, many organic compounds are unsaturated. We saw in Alkanes that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons, compounds made of only carbon and hydrogen atoms where carbon makes only single bonds.
#ALKENE HYDROCARBON WITH 6 CARBONS AND DOOBLE BONDS HOW TO#
How to name alkenes using IUPAC organic nomenclature.How to test for alkenes in a chemical reaction.The major uses and properties of alkenes.The definition of an alkene and their general formula.Identify the mistake in each one, and correct it to give the correct IUPAC systematic name. Interpret IUPAC systematic names of chemicals by applying organic nomenclature.Apply organic nomenclature to draw structural formula of alkenes.ĭraw the structural or skeletal formula for the following compounds using their IUPAC systematic names.Chemical B is a simple hydrocarbon with three carbon atoms in a straight chain.Explain why this change was seen with chemical B and not with chemical A.What was observed when chemical B was mixed with bromine water?.In the test tube with chemical B and bromine water, there was a noticeable change in the solution. The student observed no change in the test tube with chemical A and bromine water. Recall the test to distinguish alkenes and alkanes.Ī student has solutions of two simple hydrocarbons, chemical A and B, and adds them separately to two identical test tubes containing a solution of bromine water.Study the following chemical formulae and identify which fit the general formulae of an alkene.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
